Category / Section
Restricting Users to their Own Content using Roles
Published:
1 min read
You can restrict users to their own content using the new update for the Roles feature on BrainCert.
This feature restricts new content created on or after April 15, 2016.
All other contents created before this date cannot be restricted due to the nature of granular permissions.
Roles come with 2 different permissions for courses, contents, tests, and live classes.
Shared
This is the default option and allows everyone with 'Super Admin', and 'Teacher' user types or users with specific permissions to see each other's content.
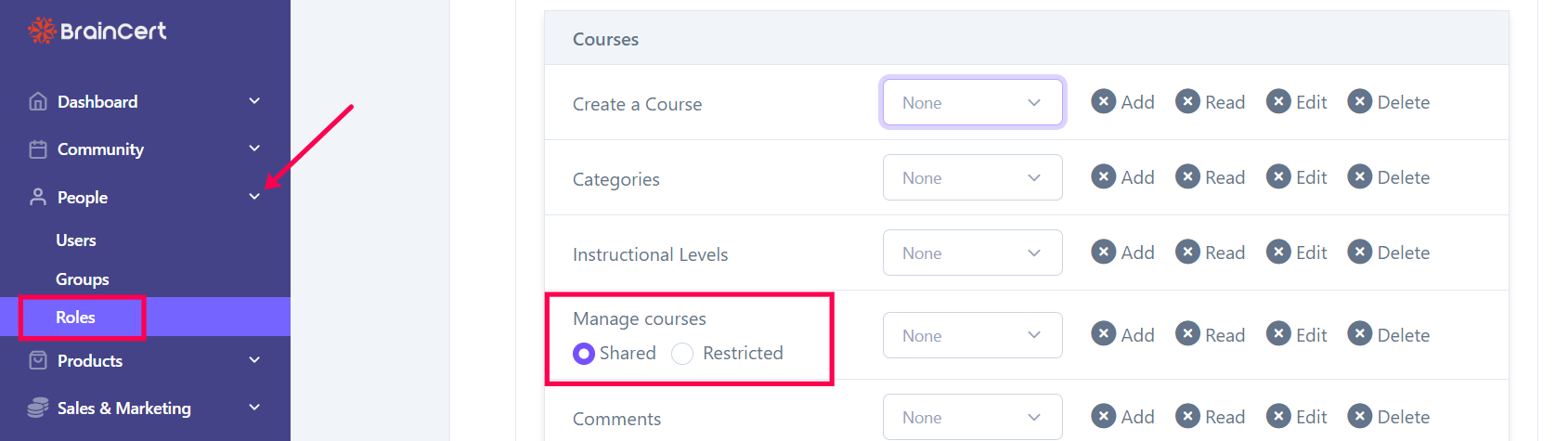
Navigate to 'Roles' under 'People' and scroll down to 'Courses'.
Shared - Shared option allows all users to see each other's content.
Restricted
Restricted - The restricted option does not show other users' content, and restricts users' own content.
Restricting the Users
Restrict the users according to your preference by selecting any option from the dropdown menu.
- None – No permission is set.
- Read – Provides read-only access to the object.
- Change - Provides all permissions permitted by read, write, edit, and save.
- Full Control - Provides all permissions permitted by read, write, edit, save, and delete.
- No Access - Denies access to all.
- In the context of user permissions, restrictions play a crucial role in shaping user access.
- Take, for example, a scenario where a user is restricted from 'Managing courses.'
- In this case, the user's access to courses will align with the specific options enabled, ensuring a streamlined and controlled experience.
- Similarly, the flexibility of these restrictions extends to various other fields, allowing administrators to tailor user access according to the organizational structure or specific requirements.
- The standout of this system lies in its adaptability – administrators can effortlessly edit existing roles, adjusting these access options, or create entirely new roles to accommodate their needs.
Refer to the link Using Roles to Create a Role-Based Navigation Structure to learn more.
